Release date: 2015-01-16
1. What is the in vitro diagnostic (IVD) industry?
IVD refers to products and services that obtain clinical diagnostic information by detecting tissues and secretions such as blood of the human body outside the human body. The “test†in the “test and inspection†commonly used in hospitals in China includes most subdivisions of IVD—such as 1 clinical chemistry, 2 immunoassay, 3 molecular diagnosis (MDx), and elemental diagnosis. , microbiological diagnosis, urine diagnosis, blood coagulation diagnosis, tissue diagnosis, hematology and flow cytometry. The first three categories are the mainstream IVD methods of medical institutions in China.
In vitro diagnosis can be divided into central laboratory and 4Point-of-Care Test (POCT) according to the application object. The main differences between the two are:
1) Immediacy and ease of operation. Because POCT does not require a central laboratory, it can be directly tested next to the patient, which can quickly diagnose, treat, and observe the disease, thereby improving the quality of medical treatment. Therefore, the penetration rate in ICU, surgery, emergency department, clinic and patient home is gradually improved.
2) Matching of reagents and analytical instruments. When using in vitro diagnostic reagents for testing, it is generally necessary to use the corresponding detection instrument to analyze the results (except for colloidal gold, biochips, etc.). The central laboratory instrument is an open system, that is, any manufacturer's reagent can obtain results on the same instrument; while the POCT diagnostic instrument is mostly a closed system (such as the blood glucose meter we are familiar with), relying on the instrument to drive the consumables to make money.
These two points mean that the POCT market demand is in full swing. It should be noted that a POCT instrument can often read diagnostic reagents made by various subdivision technologies, such as Abbott (ABT) i-STAT.
2. What is the future direction of China's IVD industry in the next 5-10 years?
In terms of technical maturity:
1 Biochemical diagnosis is well-known at home or overseas, with low technical barriers and the risk of being completely replaced by other more accurate and rapid diagnostic techniques. Domestic oligarchs Zhongsheng North, Kehua Bio, and Lidman have a monopoly on the market. The force is very strong.
2 Immunodiagnosis has been developed overseas for more than 60 years, and the technology is relatively mature. Unlike biochemistry, in vitro nucleic acid amplification technology (PCR) in immunological techniques and later emerging molecular technologies is almost equally accurate in the diagnosis and sensitivity of similar diseases, so the risk of recent substitution is small, mainly due to internal technological upgrading. ——Foreign countries are monopolizing the market and self-upgrading; while the domestic market is in a big reshuffle period, it can only be ignored when the foreign oligarchy upgrades the rhythm.
3 molecular diagnosis, also known as genetic diagnosis, is superior to immunodiagnosis in that it can measure genetic diseases. Its technology is divided into nucleic acid diagnosis (NAT) and biochip. The former mainstream PCR technology is said to be lower than the current mainstream immune technology. Low, the domestic market is in the situation of “pseudo-oligarchs really red seaâ€; but the latter technology is still immature, the development cost is very high, and it is very difficult. Although it is the future development direction, the price has always remained high, so the usage is high. Can't zoom in in the short term. In terms of foreign markets, this piece is now a blue ocean, and there are many small enterprises that are shining, such as Wanji Inheritance (MYGN), which creates the Jolie effect.
Different from other biological products industry (especially the blood products industry), the IVD industry has not received any substantial policy protection in China (except for nucleic acid diagnostic products involving blood screening), so under the promotion of multinational giants, domestic IVD products The use and research and development are still relatively good, probably about 5-10 years later. Therefore, it is necessary to refer to the overseas IVD industry structure to judge the future situation in China.
As shown in the figure below, as of 2011, the overseas in vitro diagnostic reagent market is dominated by other categories dominated by 4POCT, with 1 biochemical and 2 immunological products accounting for only 40%, and 3 molecular diagnostics accounting for nearly 11%; In the market, other categories accounted for only 13%, clinical biochemical and immunological diagnostics accounted for as much as 67%, and molecular diagnostics accounted for 5%.
According to overseas development experience, in the past four years, the average growth rate of biochemicals has been the lowest, at 6%, and its market share is facing the risk of being compressed, especially in China, which is still the second largest variety. The effect has not yet fully emerged, so its domestic growth rate is expected to be lower than the industry average. 2 Immunodiagnosis has achieved double-digit growth in revenue (average growth rate of 11%) in the global market due to continuous technology replacement and high cost performance. In China, immunodiagnosis has replaced 35% of the mainstream market share of clinical biochemistry. Because molecular diagnosis is difficult to rapidly spread in the short term due to the influence of technology and cost, the mainstream status of immunodiagnostic reagents will remain for a long time. It is also expected to be faster than the industry level. The 3 molecular diagnostics started early on the global level, the technology is becoming more mature, and the demand has been released rapidly, with an average growth rate of about 10%. The average annual growth rate of this segment in China is as high as 20%. 4 Another large-scale subdivision is POCT, and the domestic market share is only 1/3 of the global market share.
In summary, in the next 5-10 years, the share of China's IVD market will gradually tilt toward molecular diagnosis and POCT.
3. What is the demand for China's IVD industry?
The capital market's enthusiasm for the IVD industry may be aware that its demand side will grow rapidly with consumption upgrades, urbanization and new medical reforms: as the country with the largest population, the market size of China's IVD reagents is expected to be only 155 in 2013. 100 million yuan, equivalent to $ 2.45 billion, accounting for only 4.8% of the global market. Another frequently said piece in the industry is that “China's in vitro diagnostic products use only US$1.5 per year, while the per capita use of developed countries reaches US$25 to US$30. This shows that China's in vitro diagnostic market is still growing.â€
3.1. Caveat: The optimistic demand for IVD products is risky because some sub-requirements are too small to trigger the development of the entire IVD industry; some demand side faces transformation bottlenecks; some demand is actually shrinking.
An example of a smaller demand is blood screening. Blood screening is mainly for the blood sector testing of blood, including various blood stations and blood products manufacturers. The blood screening reagents are calculated according to the blood collection of 4000 tons in each blood station and pulp station in 2012, 0.3kg per blood, and a total of 25 million blood screening tests. The price of each blood screening is 30~70 yuan, and the blood screening market size is about 10 100 million yuan, accounting for less than 0.5%. Although the current blood source screening is carried out by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent reagent (ELISA) to the PCR reagent, but because the threshold of the PCR reagent is not high, the demand for this fine molecule is increasingly showing the situation of the Red Sea. The only good thing may be that the state accepts and reviews the blood products according to the drugs, and needs to be approved to help the more brand-name manufacturers to maintain market share.
An example of a transformation bottleneck is the Third Party Lab (ICL). ICL is a professional central laboratory for hospitals to outsource inspection services to save medical expenses. It is a mainstream and mature business model for the in vitro diagnostic market in the United States and Europe, and accounts for about 40% of the in vitro diagnostic market in foreign countries. . However, in China, because the current medical reform program emphasizes that the drug control price has reduced the profit margin of the hospital, most hospitals can only switch to the use of the laboratory to generate income, so the lack of motivation for the outsourcing of diagnostic projects, the development of ICL encountered a certain bottleneck. At present, the largest ICL company is Guangzhou Jinyu, and its income is about 1 billion yuan. The income of Dean Diagnostics, Aidi Kang, Daan Gene and Kangsheng Global is between 1.5 and 300 million yuan. The total income is about 2 billion, the total scale of other companies is about 500 million yuan, and the total size of ICL is about 2.5 billion yuan.
An example of a real shrinking demand is hepatitis B diagnosis. In 2010, the country began to cancel the test of hepatitis B in the mandatory medical examinations for students such as schooling and employment, which led to the fact that Kehua Bio has not slowed down yet.
3.2. Future demand is expected to be heavy: 1 physical examination needs. Previously, the medical examination was limited to mandatory special medical examinations for employment, military participation and schooling, and it was a non-profit project. In recent years, as medical treatment has been upgraded from disease treatment to disease prevention, physical examination has become a profitable project, and more and more Chinese people Start accepting the idea of ​​“paying for healthâ€. According to data provided by Frost & Sullivan, China's health check-up market has reached a market size of about 50 billion in 13 years. If the proportion of in vitro diagnostic items is about 20%, the diagnostic reagent for physical examination has reached about 10 billion. In addition, the preventive medical examination is not within the scope of medical insurance, and it is not in the field of national fiscal expenditure. Therefore, the in vitro diagnostic items for physical examination are generally market-priced, and the terminal has a large profit margin. For the medical examination market, Phadia's allergen screening ImmunoCAP, Wanji genetic tumor diagnosis chip (gene chip), autoimmune disease diagnosis chip, etc. are all worthy of attention.
2 Household consumption (OTC) demand. At present, the research and development direction of diagnostic reagents in China mainly meets the needs of medical diagnosis, and there is no diagnostic product for household consumption. Therefore, the current OTC diagnostic products account for only about 6% of the overall market, mostly with pregnancy test sticks and blood glucose meters. the Lord. As the income of residents grows, the proportion of the elderly increases, the emphasis on health, prevention is more important than treatment, and early detection of early treatment, the market demand for OTC products will accelerate, and the diagnostic reagents for household consumption are often “instrumentationâ€. Sales in the form of “reagents†(“toolholder bladesâ€) provide a stable cash flow for production companies. For domestic enterprises, on the one hand, they can take the low-cost and innovative 'cottage' road, and compete with overseas giants in terms of low-end blood glucose meters, such as Sannuo Bio has successfully occupied the developing market; on the other hand, it can try to do domestic 'Gao Da Shang', such as Libang Instruments, introduced the former i-STAT company senior scientist Lin Chao from the United States, made the first POCT blood gas / electrolyte analyzer in China, and will carry out research and development upgrades, through the selection of different test cards. Realize the detection and analysis of cardiac markers.
3 The needs of the grassroots health market. The state’s fiscal expenditure on health care has been tilted towards the primary health system in recent years. The nearly 100 billion investment has improved the hardware conditions of the primary health system and the ability to purchase semi-automatic/automatic in vitro diagnostic instruments for in vitro diagnostics. Previously, overseas giants have judged that China will follow the developed countries, such as the United States and Europe, and vigorously develop ICL to provide services to unqualified primary medical institutions, so the demand for high-end IVD diagnostic instruments (including POCT instruments, because the price is not cheap now) There will be growth; but at present, the development of ICL in China is still concentrated in the eastern coastal areas, and there is no penetration at the grassroots level, so the health needs of the grassroots level must be solved locally. This means that foreign giants and domestic companies are currently at the same starting line in the middle and low-end IVD products, creating a better market environment for semi-automated immunodiagnostic analyzers produced by companies such as Shenzhen Mindray.
3.3. The most important demand, the growth rate and the industry growth rate are consistent: the public hospital inspection department accounts for about 89% of the IVD industry, and its demand growth will drive the development of China's IVD industry.
In general, the demand sources of the IVD industry are diversified, and the characteristics of diagnostic reagents are not the same. In addition, in vitro diagnostic reagents are disposable consumer goods, and the market demand for stocks will not shrink. Most of the market demand (such as cancer screening gene chips for high-end medical examinations) has not been met, and there are still many unsaturated markets to be developed. If you can seize the opportunity to launch new products in these unsaturated markets, then the company will face a blue ocean.
4. Why do you choose the IVD industry according to the logic of buying medicines and not buying medicines?
This is an extension of the industry needs of the previous section. Consumption upgrading, urbanization and new medical reforms will promote the development of China's pharmaceutical industry in the future, but why do you think that the medium-term demand growth rate of medical devices/services will be higher than that of the pharmaceutical industry as a whole? Why do you think that the IVD industry will be the most beneficial micro-molecular industry?
The main pressure facing China's current fiscal expenditure on health care comes from the excessive growth of drug costs, and the proportion of drug expenses in total health expenditure is too high. In terms of drug costs, in 2011, China's drug costs were nearly 94 million yuan, a year-on-year increase of 24%. In 2009, China's drug costs increased significantly, and maintained a high growth rate for the next three years. The proportion of drug expenses in total expenses increased significantly. In 2011, this proportion reached 42%. This ratio is significantly higher than that of the major developed countries. Taking the 2007 data as an example, the United States has the lowest proportion of medicines, only 12%, and the highest proportion of South Korea is only 25%. The decline in the proportion of medicines will be the trend of the development of health expenditure in China in the future. The State Council announced in April 12 that the main work arrangements for deepening the reform of the medical and health system in 2012 clearly pointed out that one of the key directions of the new medical reform is to adjust the price of medicines and eliminate the policy of adding medicines.
Compared with the government's strong control over the procurement mode and price of drugs, the IVD industry is relatively loose. Most provinces have not even adopted unified bidding for IVD testing reagents with low price of single products. The diagnostic reagents required by hospital laboratory are self-purchasing. The relevant departments also did not stipulate the hospital's inspection income ratio. Compared with the 15% increase rate of medicines, the gross profit rate of the inspection is about 50%. Especially after the public hospitals gradually cancel the drug addition, the medical institutions will gradually pay more attention to the inspection business. The contribution to profit is expected to be one of the important driving forces for the expansion of the IVD market in the future.
The IVD industry may be affected by factors such as total prepayment in the medium term, but it is expected that the policy and medical insurance will have a relatively small possibility of controlling the inspection costs in the short term, mainly due to the fact that it is more difficult to be practical. Currently, the fees are relatively high, such as MR. The price of the inspection will be adjusted (in early 2012, the price of medical services in each province was mainly reduced by radiology inspection items), but the price reduction of inspection items was small. (From the "over-diagnosis" problem that the US government has not yet solved, it can be known that the inspection items are too subdivided and the price control is more difficult.)
The market-wound system may affect the overall decline in the revenue of pharmaceutical companies. The impact on the IVD industry may only be “price dropâ€. The price drop is because the diagnostic reagent products are included in the cost end of the profitability of medical institutions. From the perspective of economic efficiency, medical institutions are more inclined to choose products with cost-effective advantages. The increase is due to the mature disease-based diseases in the United States. Mode, to a large extent, diagnostic reagents are an important reference for doctors to provide diagnostic protocols to patients, so they are used more frequently.
5. Industry chain and supply of China's IVD industry
The IVD industry is divided into IVD reagents (also known as IVD kits), IVD instruments and IVD consumables. The former accounts for more than 82% of the entire industrial market, and the latter two add up to about 18%.
The IVD reagent industry chain includes 1 upstream raw material link: raw materials mainly rely on imports, Lidman will be one of the core competencies for preparing antibodies for immunodiagnostic raw materials, and its self-produced antibodies in IPO are better than similar ones. IVD reagent manufacturers can save about 40%-60% in cost. 2 Upstream research and development: Mainly copying foreign products. 3 upstream production: assembly of raw materials. China has mastered the above-mentioned production raw materials, the market supply is sufficient, the price fluctuation is not large, and the in vitro diagnostic reagent industry has a strong cost transfer capability, which can effectively avoid the cost pressure from the supply of raw materials, so the profitability of the enterprise is stable. 4 mid-stream sales links: companies can choose to build their own channels, through professional distributors or with large-scale marketing units in the industry chain (such as in vitro diagnostic equipment manufacturers) to complement their advantages to sell their products. According to the data provided by the IVD Special Committee, there are about 300 to 400 in vitro diagnostic reagent manufacturers in China, including nearly 200 enterprises above designated size, but only about 20 enterprises with annual sales income exceeding 100 million yuan. With fewer varieties, and the country has not yet clarified the procurement mode of diagnostic reagents for downstream use, upstream manufacturers often need strong dealers to help sell the research, so the midstream sales are extremely strong. 5 downstream use links: According to the use, it can be roughly divided into three parts: medical test, household (OTC) and blood source screening (blood screening). Among them, medical tests include hospitals, medical centers, independent laboratories (ICL), and epidemic prevention stations. The hospital is the largest downstream demand side in the in vitro diagnostic industry, accounting for 89% of the total market size, and third-party laboratories (ICL) account for about 1%. The hospital and ICL have a business overlap with the medical examination center, and the medical examination market accounts for 4%. OTC accounts for 6%, and the blood screen market accounts for less than 0.5%.
The two parallel industries related to in vitro diagnostic reagents are in vitro diagnostic instruments and in vitro diagnostic consumables (such as $ Yangpu Medical (SZ300030) $ blood collection tube), and only with them can finally produce a diagnosis (except immune colloidal gold) Method and immunoblotting). 10 years ago, in China's in vitro diagnostic equipment, the high-end automatic analyzers for secondary and tertiary hospitals and ICL were basically imported, while the manual and semi-automatic analyzers used in domestic primary hospitals were mostly made in China. Shenzhen Mindray, Dyre Medical and Shenzhen Lan Yun. In the past two years, inspired by the profit model of multinational in vitro diagnostic companies providing diagnostic instruments semi-free and relying on the sale of matching diagnostic reagents, the boundaries between domestic diagnostic instruments and diagnostic reagent companies have become increasingly blurred, and reagent manufacturers have passed OEMs. Manufacturers (such as Nanjing Laura) have customized, disassembled and imitated overseas products, and cooperated with multinational giants (such as Sysmex and Kehua Bio, Biorad and Beijing Wantai), and also have their own brand of instruments.
At present, diagnostic instruments are classified into three categories: fully open, semi-open, and fully enclosed platforms according to their compatibility with diagnostic reagents. The enzyme-free (ELISA) diagnostic instruments in biochemical diagnostic instruments and immunodiagnosis are mostly open, and the specifications of the corresponding diagnostic reagents (boxes) are also consistent; the semi-open platform is represented by Roche's Elecsys electrochemiluminator. In addition to reading its original electrochemiluminescence immunodiagnostic reagent (ECLIA), other manufacturers' diagnostic reagents can also be analyzed and tested; the fully enclosed platform is generally a POCT instrument, and the instrument can only read the reagents that match it. For example, Alere's Tiage, the domestic Sannuo bio-glucometer is also this model. In China, other IVD instruments other than POCT are generally open platforms.
Through the above description, you should be able to see how much the Chinese IVD industry relies on multinational giants in the upstream and instrumental sectors, and it will not be surprised that foreign manufacturers control more than 75% of the overall market share. The remaining 25% of the market share, corresponding to about 6 billion yuan, by more than 300 domestic companies compete for each other, it can be seen that the competition on the supply side is still relatively fierce. At present, Kehua Bio-revenue, which has the largest IVD revenue among listed companies, is less than 1 billion yuan. Its self-produced diagnostic reagents plus self-produced instruments and consumables have an income of about 550 million yuan and a market share of about 4%.
Of course, according to the market segment, some companies still have a relatively stable market position because of their deep moat. For example, $Bohui Innovation (SZ300318)$ in trace element detection has recently been involved in the field of nucleic acid diagnostics; for example, the Daan gene in the field of molecular diagnostics.
6. Vertical integration! Horizontal integration!
For companies in the IVD industry, everyone is busy consolidating resources, because overseas giants are also so powerful (fog). Moreover, in China, there have been companies that have adopted ICL from the upstream production link to the mid-stream sales link to the end-use link. In the future, with the liberalization of private hospitals and the popularization of profitable medical institutions, there will be strong IVD companies (perhaps Is it possible for Fosun Pharma (SH600196)$ or China Resources Business to integrate the resources of integrated manufacturers, distributors, hospitals and medical examination centers to provide one-stop service (but will it really be more economical? Doubt).
The ideal vertical integration mode is the development of IVD reagent companies to IVD instruments, and vice versa. This is one of the success factors of multinational giants, because it can achieve the ideal model for selling instruments to drive the sale of test reagents, thus effectively resisting the industry. risk. There is also a reason why it is very important in foreign countries to be very tasteless in the country, that is, by developing new diagnostic markers by IVD reagent manufacturers, and developing semi-open or fully enclosed IVD instruments for the original markers, in the case of certain diseases. The diagnosis creates a technological monopoly that greatly enhances the competitiveness of its products. A little story of hearsay: BNP, a heart failure marker developed by Biosite, is the most sensitive and accurate indicator for diagnosing heart failure, but Biosite only licensed Beckman Coulter's in vitro diagnostic instrument to use this indicator for companies such as Roche. Diagnostic instruments are very difficult to sell; until Roche developed a similar NT-proBNP marker, it was considered a reincarnation.
Horizontal integration, access to more core technologies through mergers and acquisitions is the second success factor of multinational giants: overseas, externally seeking technology has become part of the in vitro diagnostics market, especially in the past few years when test technology has become more complex. on. New in vitro assays include biochips, protein templates and gene synthesis, disease calculations, and bioinformatics. Therefore, M&A has become a way for companies to build product lines. On the other hand, for small IVD companies, marketing to new products is often more effective by selling technology to multinational giants with mature market experience.
In China, in 2012, Renfu Medicine and Xinhua Medical entered the IVD field through mergers and acquisitions. As early as 2005, Shenzhen Pico was fully acquired by Qiagen in Germany. The entire diagnostic reagent industry has begun to have some integration, but the current market concentration is still Lower. Therefore, mergers and acquisitions among domestic enterprises are the general trend in the future, which will be more conducive to listed companies with strong capital strength and more financing channels.
7. Several characteristics of good domestic IVD companies
1 Introduce products that meet market demand, but pay attention to avoiding the Red Sea! (such as the recent IVD kit and IVD instruments related to PCR and immunochemiluminescence; such as blindly opening ICL);
2 The products are similar to multinational giants in terms of specificity, sensitivity, detection range and analysis time;
3 Enterprises that have control over the sales channels have better sales models that use instrument-driven or service-driven reagent sales;
4 Enterprises with technical research and development capabilities, or companies that can complement each other with overseas companies. But more important is the experience of quickly getting the drug number;
5 For POCT companies, multiple indicators are often more important than accuracy;
6 cost control is appropriate, the price has an advantage in similar products, because the future must be unified bidding.
Source: Snowball
New product of U85 micro laser distance sensors use highly focused class 2 laser to detect objects or measure distances, and can return a measured value via varieties intface( serial, usb, rs232, rs485, bluetooth etc.). The electronic distance sensor is a very small Laser Distance Sensor, but high resolution up to 1mm and long distance measuring sensor - teachable measuring range of up to 30m. Extremely accurate distance sensing sensors, errors down to ± 1mm. And the mini sensors and measurements support continuous measurement function, great for compact solutions(eg: robots) with the smallest Laser Distance Sensor of the world!
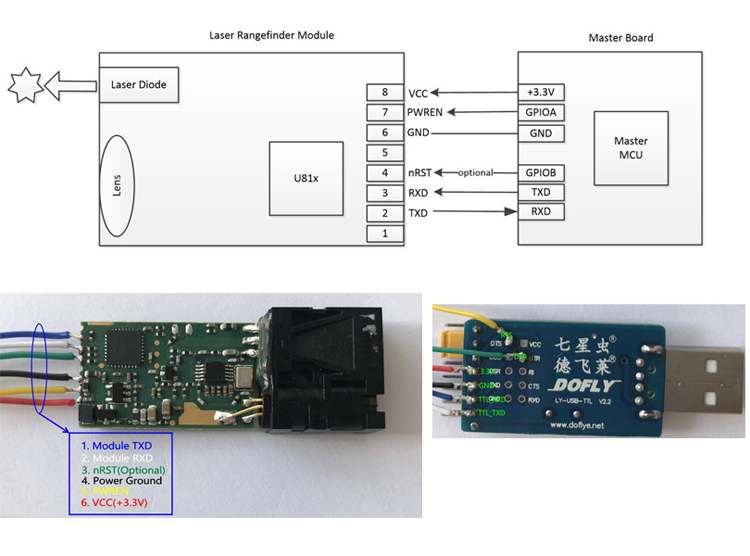
Parameters of U85:
Accuracy
±1 mm (0.04 inch)
Measuring Unit
mm
Measuring Range (without Reflection)
0.03-20m/0.03-30m
Measuring Time
0.1~3 seconds
Laser Class
Class II
Laser Type
620nm-690nm, <1mW
Size
41*17*7mm (±1 mm)
Weight
About 4g
Voltage
DC2.0~3.3V
Electrical Level
TTL/CMOS
Certifications
CE, FCC, RoHS, FDA
Operating Temperature
0-40 ℃ (32-104 ℉ )
Storage Temperature
-25~60 ℃ (-13~140 ℉)
Mini Laser Distance Sensor,Optical Laser Distance Sensor,Smallest Laser Range Sonsor,Laser Measuring Sensor
Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.jrt-measure.com