The biofilm is a group of organized bacteria that is formed by the extracellular macromolecules of bacteria. It is usually composed of extracellular polymers, including proteins, DNA and polysaccharides. The biofilm can help bacteria resist the anti-antibiotic and host immune defense mechanisms. It is worth noting that biofilms can adhere to medical devices such as catheters, cardiac implants, and inadequately sterilized surgical tools, resulting in hospital-acquired infections.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is widely distributed in the skin, intestines and respiratory tract of nature and normal people, and is one of the common pathogenic bacteria in clinical practice. Pseudomonas aeruginosa can produce a variety of virulence-related substances, is more resistant to chemical drugs than general Gram-negative bacteria, and can form a strong biofilm in a variety of environments. Moreover, the bacterial biofilm is a life phenomenon in which bacteria adapt to the natural environment, so it is important to understand the genetic regulation of biofilm production and maintenance. Studying its formation mechanism is expected to find effective antibacterial drugs and improve the body's immune defense capabilities.
Professor Tung T. Hoang et al. used Nicoya 's local surface plasmon resonance technique to explore the complex gene regulatory network related to the formation and maintenance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. The binding kinetic data obtained by OpenSPR quantitatively verified the transcriptional regulatory factors PA1226, PA1413. They form a stable complex with their target DNA binding sequences to regulate the formation of biofilms. The related research "Novel dual regulators of Pseudomonas aeruginosa essential for productive biofilms and virulence" was published in MOLECULAR MICROBIOLOGY.

The researchers first used transcriptome analysis to screen hundreds of transcriptional regulators that may be involved in the formation of P. aeruginosa biofilm. Combined with crystal violet staining and in vivo infection experiments, it was confirmed that gene insertion deletion of PA1226 protein can significantly reduce biofilm formation. . Further ChIP-seq, microarray analysis and gel retardation analysis indicated that there is another helper regulator that mediates the interaction between PA1226 and the target DNA. Immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry revealed that PA1413 may coordinate with target DNA in PA1226.
To verify whether PA1226 synergizes with PA1413 to control target DNA, the researchers used Nicoya's OpenSPR local surface plasmon resonance technique to quantify their interactions in real time. First, the His-tag PA1413 protein was coupled to the NTA chip, and then the interaction between PA1226, DNA, PA1226-DNA mixture and PA1413 was examined. When PA1226 or DNA was loaded alone, no interaction was detected, and the PA1226-DNA mixture produced a very significant concentration-dependent binding curve. The software analysis gave an equilibrium dissociation constant of 0.31 μM. This data scientifically proves that PA1226 is PA1413 synergistically regulates the target DNA, thus uncovering the mechanism of biofilm formation, opening a door for the development of antibacterial drugs or the body's immune and epidemic prevention mechanism.
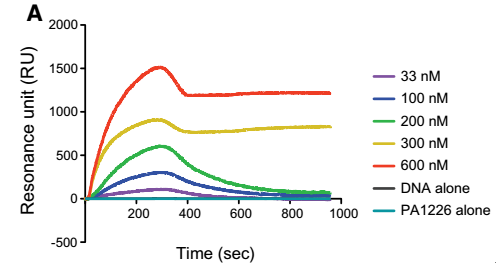
OpenSPR rapidly confirmed that the regulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation requires PA1226, PA1413, and DNA complexation.
The OpenSPR molecular interaction analyzer can detect the interaction between molecules in real time without label, and determine whether the interaction between the molecules is indirectly or directly through the data to determine the relationship between the complexes, so as to further explain the life mechanism.

Advantages of the Nicoya OpenSPR Molecular Interoperator Transcriptional Regulation Complex:
• Real-time no mark---reducing the cost of the experiment, which is conducive to the design of the test experiment;
• Easy to operate - 1 hour to control;
• Complete kinetic parameter detection - Ka, Kd, ​​KD;
• Renewable chips – facilitate rapid detection of direct or indirect interactions between molecules and interactions between complexes;
• High precision – detection is not affected by temperature and buffer refractive index;
Two-Piece Colostomy Bag,Internal Colostomy Bag,Colon Cancer Colostomy Bag,Bowel Removal Colostomy Bag
Wenzhou Celecare Medical Instruments Co.,Ltd , https://www.wzcelecare.com