Foreword
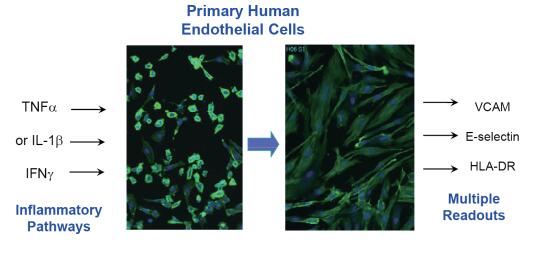
An important step in the inflammatory response is the specific binding of cell surface antigens to immune cells in blood vessels. Therefore, timely monitoring of these molecular changes, such as VCAM, E-selectin, and HLADR on endothelial cells, can provide effective physiological indicators for cell-level inflammation models.
We used multi-channel fluorescence to read the inflammatory markers on the surface of human primary cells, and on this basis we evaluated the regulation of inflammatory responses by different mediators. For example, after primary endothelial cells (HUVEC) are stimulated with inflammatory factors (TNF or IFN), expression of inflammatory markers on the cell surface can be quantified by detecting the total fluorescence intensity of the pre-stained antibody to which it binds.
We compared the IsoCyte Scanning Cell Counter with the SpectraMax® M5 Microplate Reader on multiple indicators such as increasing intergroup differences, repeatability and throughput. Multi-channel readings can be used to examine the effectiveness and toxicity of anti-inflammatory compounds, as well as to investigate mechanisms by selectively inhibiting inflammatory markers activated by different signaling pathways.
Inflammation experiment
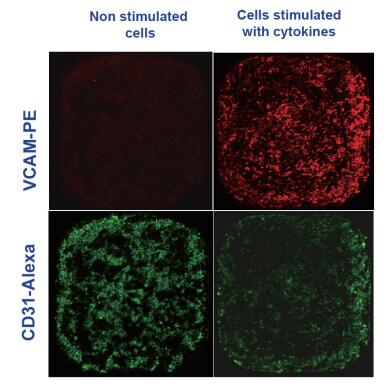
HUVEC cells (lonza) were stimulated with inflammatory factors (TNF, IFN; R&D) for 24 h. The cells were stained and labeled with the specific binding of pre-stained antibodies and adhesion molecules using the method recommended by the BD company instructions.
Selected antibodies include:
PE-conjugated anti-CD106 (VCAM),
APC conjugated anti E selectin
APC-conjugated anti-HLA-DR
AF488-conjugated anti-CD31 (PECAM)
method
Fluorescence detection of inflammation markers
The IsoCyte-DL scanning cell counter platform in the demonstration is equipped with 20mW 488nm and 40mW 640nm lasers. A 488-nm laser with a 510-540 nm bandpass (bp) filter can be used to detect Alexa Fluor® 488 (AF488)-labeled cells; a Phycoerythrin-labeled cell requires a 560-610 nm bp filter ( Ch3); APC detection requires 640 nm excitation and 660-720 nm emission filter. Images were acquired by 5*5 micron sampling and scanning was performed on 96-well or 384-well plates in 5 min.
The SpectraMax® M5 Multiwell Plate Reader contains 488 nm excitation and 530 nm scattering (dichroic mirror 515 nm) to detect Alexa Fluor® 488-labeled cells, and 590 nm (dichroic mirror 550 nm) to detect Phycoerythrin-labeled cells.

Results and discussion
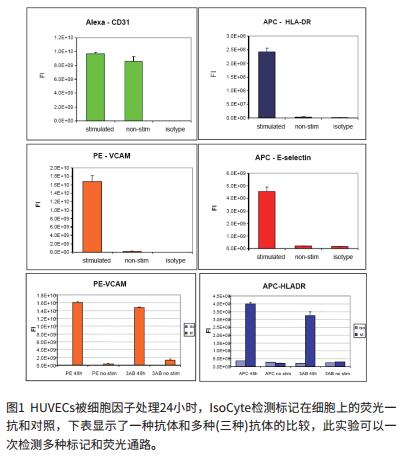
Detection of expression of inflammatory markers with SpectraMax® M5
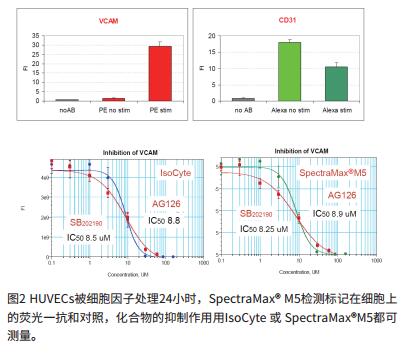
Anti-inflammatory compounds inhibit adhesion molecules
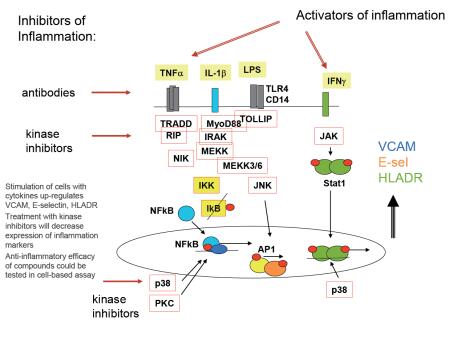
Comparison of potential anti-inflammatory compounds
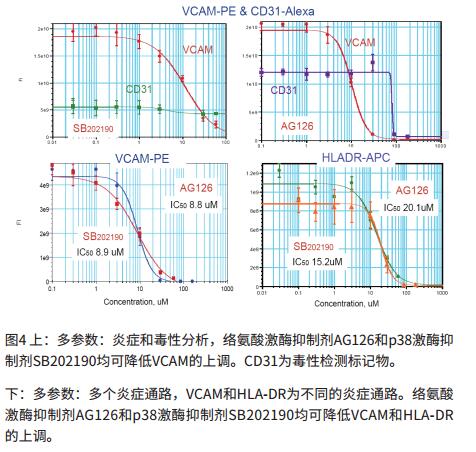
Multichannel inflammation experiment
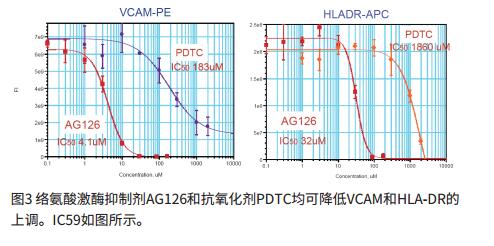
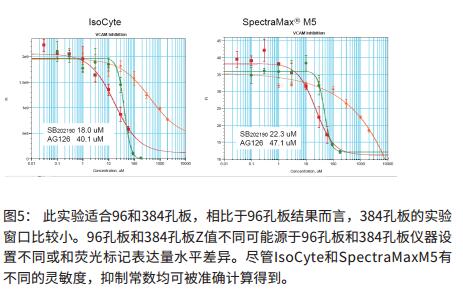
High-throughput experiments to evaluate the efficacy of anti-inflammatory compounds
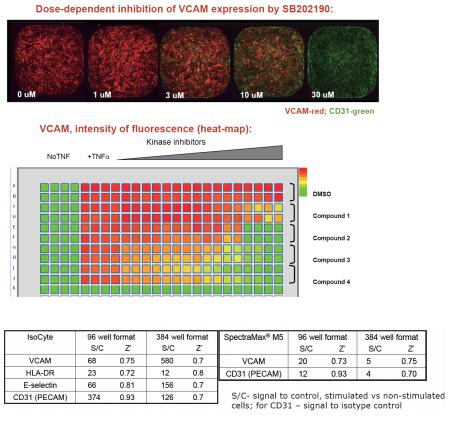
to sum up
- We can effectively evaluate the efficacy of anti-inflammatory compounds by detecting the binding of labeled antibodies to adhesion molecules.
- We have tested the expression levels of cellular inflammatory markers such as VCAM, E-selectin, HLA-DR, CD31 under various treatment conditions for HUVEC cells in a combination of various inflammatory and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Up-regulation and down-regulation of inflammatory markers can be effectively monitored using multi-channel IsoCyte or SpectraMax® M5.
- Our data include the use of three known anti-inflammatory compounds: AG126, SB202190 and PDTC to assess the efficacy of anti-inflammatory molecules.
- In high-throughput compatibility mode, we can test the efficacy of anti-inflammatory compounds using multi-channel inflammatory assays at the 96-well and 384-well plate levels.

Freeze-Dried Coffee,Cold Brew Freeze-Dried Coffee,Freeze Dried Cold Brew Coffee
Biodep Biotechnology Co. ,Ltd. , https://www.mbioda.com